Insight into the Upcoming New Individual Income Tax Law
A Remarkable Revolution in Chinese Taxation
深入了解即将出台的新个人所得税法
中国税收的显着革命
Authors:
Manuel Torres, Managing Partner of Garrigues China
Diego D’Alma, Partner of Tax Department
Cynthia Zhou, Tax Associate
 中华人民共和国的个人所得税(“IIT”)法(“中国”或“中华人民共和国”,不包括香港,澳门和台湾)于1980年首次出台。2011年对中国的现行个人所得税法进行了修订。 最近对2011年IIT法的修订得到了全国人民代表大会常务委员会的批准(2018年8月31日),这是中国个人所得税法第7次修订,将于2019年1月1日起生效。 (2018年10月1日实施的工资收入的累进IIT率变化除外)。
中华人民共和国的个人所得税(“IIT”)法(“中国”或“中华人民共和国”,不包括香港,澳门和台湾)于1980年首次出台。2011年对中国的现行个人所得税法进行了修订。 最近对2011年IIT法的修订得到了全国人民代表大会常务委员会的批准(2018年8月31日),这是中国个人所得税法第7次修订,将于2019年1月1日起生效。 (2018年10月1日实施的工资收入的累进IIT率变化除外)。
在2018年为实现国际税收协调和适应中国过去十年劳动力成本增加而实施的IIT法是一个革命性的成就。 它计划缩小贫富差距,并加强各政府部门之间的信息共享。 本文概述了2018 IIT法的变化,并强调了对在中国工作的员工(包括中国和外国员工)及其中国雇主的潜在影响。
2018年的IIT法 是中国税收的一项重大革命,它将以多种方式对纳税人和扣缴义务人产生重大影响:
- 具有中国收入和海外收入的税收居民将面临在中国对全球收入征税的挑战。
- 随着税务居民评估期缩短,外籍人士更有可能成为中国税务居民。
- 实施2018 IIT法后,中低收入的中国员工将从工资收入中节省大量的个人所得税,而高收入的中国员工可能受益有限。
- 有资格获得额外特殊减免项目的中国员工可以进一步减少他们的IIT负担。
- 计划移民到其他国家的中国人应特别注意,税收状态可能对移民计划产生不利影响。
 Individual Income Tax (“IIT”) Law of the People’s Republic of China (“China” or “PRC”, excluding Hong Kong, Macau and Taiwan) was first introduced in 1980. The prevailing IIT Law of PRC was revised in 2011 (“IIT Law 2011”). Recent revision made to the IIT Law 2011 was approved by the Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress on August 31st, 2018 (“IIT Law 2018”), which is the 7th revision on IIT law in China and will be effective from January 1st, 2019 (except for the changes in progressive IIT rates for salary income to be implemented on October 1st, 2018).
Individual Income Tax (“IIT”) Law of the People’s Republic of China (“China” or “PRC”, excluding Hong Kong, Macau and Taiwan) was first introduced in 1980. The prevailing IIT Law of PRC was revised in 2011 (“IIT Law 2011”). Recent revision made to the IIT Law 2011 was approved by the Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress on August 31st, 2018 (“IIT Law 2018”), which is the 7th revision on IIT law in China and will be effective from January 1st, 2019 (except for the changes in progressive IIT rates for salary income to be implemented on October 1st, 2018).
IIT Law 2018 is a revolutionary step towards harmonization of international taxation and is an adaption in response to the increasing labor costs over the past decade in China. It also intends to minimize wealth gap and enhances information sharing between various government authorities. This article provides an overview of changes in IIT Law 2018 and highlights its potential consequences on employees (including both Chinese and foreign employees) working in China and their Chinese employers.
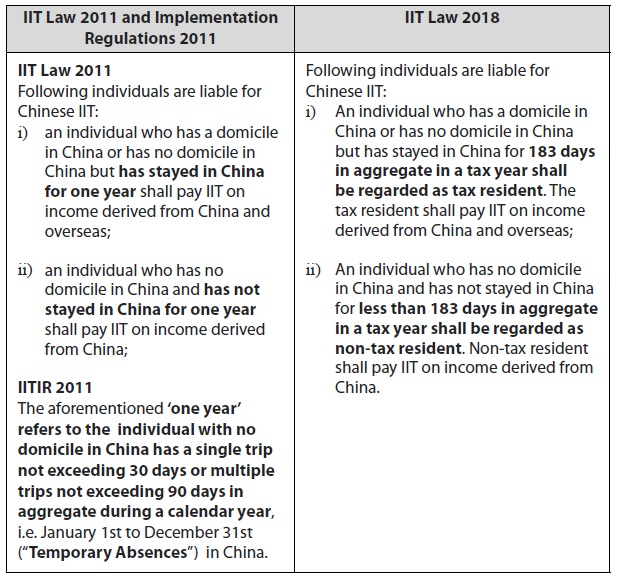
1. Definition Of Tax Resident
IIT Law 2018 clearly defines the concept of tax resident and non-tax resident, which have been widely used in international taxation, but this concept was not explicitly addressed in the IIT Law 2011. In addition, the IIT Law 2018 has shortened the time period of being qualified as a tax resident in China from one year to 183 days in a tax year (i.e. January 1st to December 31st). There would be a direct impact on foreign expatriates working in China (“Expatriates”), who would be more likely to become a tax resident in China after the implementation of IIT Law 2018.
Implementation Regulations on IIT Law 2011 (“IITIR 2011”) has stipulated that Expatriates living in China for one year or more but lasting no more than five consecutive years could be exempted from overseas sourced income paid outside the territory of China (e.g. salary paid by an overseas employer, overseas investment income and rental income etc.). Otherwise, expatriates living in China for more than five consecutive years are taxable on worldwide income from the sixth year in China (“5 Year Rule”). At present, many expatriates break the 5-Year Rule by arranging a single trip of over 30 days or multiple trips over 90 days in a particular calendar year within a 5-year interval so as to avoid being taxable on worldwide income in China. As detailed implementation report on IIT Law 2018 has not been issued yet, it is uncertain whether the 5-Year Rule would be maintained or revised. Expatriates are suggested to pay special attention to the new implementation rules on IIT Law 2018 for the planning of tax resident.
The below table is a comparison of IIT law 2011 and IIT Law 2018 regarding the tax resident rule in China.
2. Consolidating Income, Increasing Statutory Deduction and Adjusting IIT Rate
Consolidating Different Types of Income
IIT law 2018 has reduced the types of income from 11 categories to 6 categories. The below table illustrates main changes in the consolidation of income.
 Increased Statutory Deduction for Comprehensive Income
Increased Statutory Deduction for Comprehensive Income
Labor costs in China have been significantly increased over the last decade. According to the data sourced from the official website of Shanghai Municipal Human Resource and Social Security Bureau, average annual salary in Shanghai has doubled during the last eight years. The statutory deduction (RMB 3,500 for Chinese employee and RMB 4,800 for expatriates, which is applicable on a monthly basis) and the seven level progressive IIT rates for salary income have not been adjusted since 2011.
The IIT Law 2018 has made the following changes:
- Statutory deduction for tax residents has been increased to RMB 60,000 per annum on comprehensive income.
- Statutory deduction for non-tax residents has been increased to RMB 5,000 per month on salary income; Income derived from independent service, manuscripts and royalties shall be taxed with no statutory deduction.
- Increased statutory deduction will be effective from October 1st, 2018.
Adjusted IIT Rates for Taxable Income
As a consequence of consolidating income, taxable income of comprehensive income and trading income would apply to two different sets of progressive IIT rates effective from October 1st, 2018.
Regarding the applicable IIT rates for comprehensive income, the applicable IIT rates under IIT Law 2018 for lower and middle income individuals (with taxable income not exceeding RMB 25,000 per month) have been extensively reduced. However, IIT rates for high income individuals (with taxable income exceeding RMB 25,000 per month) would remain unchanged in the IIT Law 2018.
 Changes in consolidating comprehensive income and IIT rates for taxable income would have minor impact on high salary income tax resident expatriates, since neither the statutory deduction nor the IIT rate has been changed dramatically. Nevertheless, influence of such changes on lower and middle income Chinese individuals may be more outstanding. Discussed below are two examples to illustrate the extent of influence -
Changes in consolidating comprehensive income and IIT rates for taxable income would have minor impact on high salary income tax resident expatriates, since neither the statutory deduction nor the IIT rate has been changed dramatically. Nevertheless, influence of such changes on lower and middle income Chinese individuals may be more outstanding. Discussed below are two examples to illustrate the extent of influence -
Example 1
A Chinese employee has monthly salary (after deducting social securities and housing fund) of RMB 20,000.
(a) IIT Rule 2018
Comprehensive income per month = RMB 20,000
Taxable income per month = RMB 20,000 – RMB 5,000 (statutory deduction) = RMB 15,000
IIT payable = RMB 15,000 *20% - RMB 1,410 = RMB 1,590
(b) IIT Rule 2011
Taxable income per month = RMB 20,000 – RMB 3,500 (statutory deduction) = RMB 16,500
IIT payable for salary income = RMB 16,500 *25% - RMB 1005 = RMB 3,120
Lower and middle income Chinese employees would have significant IIT savings from salary income after the implementation of IIT Law 2018.
Example 2
A Chinese employee has monthly salary (after deducting social securities and housing fund) of RMB 35,000 and independent service income of RMB 20,000 per month (both are China-sourced incomes).
(a) IIT Rule 2018
Taxable income per month = RMB 35,000 + RMB 20,000*80% – RMB 5,000 (statutory deduction) = RMB 46,000
IIT payable = RMB 46,000*30% - RMB 4,410 = RMB 9,390
(b) IIT Rule 2011
Salary income per month = RMB 35,000
Taxable income per month for salary = RMB 35,000 – RMB 3,500 (statutory deduction for Chinese employee) = RMB 31,500
IIT payable for salary income = RMB 31,500 *25% - RMB 1,005 = RMB 6,870
Independent service income per month = RMB 20,000
Taxable income per month for service = RMB 20,000 * (1-20%) = RMB 16,000
IIT payable for salary income = RMB 16,000*20% = RMB 3,200
Total IIT payable = RMB 6,870 + RMB 3,200 = RMB 10,070
IIT savings on comprehensive income to high income Chinese individuals may be limited.
Similar to comprehensive income, the applicable five level progressive IIT rates for the trading income has been adjusted as follows:
 Interest, dividends, bonuses, rental income, income from sale of properties and contingency income would continue to be taxed at 20%.
Interest, dividends, bonuses, rental income, income from sale of properties and contingency income would continue to be taxed at 20%.
3. Additional Special Deduction Items
A number of prevailing IIT Laws allow special deduction of individuals’ social insurance and housing fund , enterprise annuity , tax deductible commercial health insurance and tax deferral commercial pension insurance . Further IIT Law 2018 provides a number of additional special deduction items on comprehensive income for tax residents (“Additional Special Deduction Items”), such as children’s education expenses, continuing education expenses, medical expenses for serious diseases, interest for housing loan and rental expenses.
Detailed implementation rules on the Additional Special Deduction Items have not been introduced. It is expected that the IIT costs to lower and middle income tax residents may be further reduced to a certain extent from January 1st, 2019.
4. Anti-Avoidance IIT Rules On Individuals
Following the implementation of information exchange on financial accounts between China and other participated countries or jurisdictions by Chinese tax authorities, anti-avoidance IIT rules on individuals are newly introduced in the IIT Law 2018.
Tax authorities are empowered to make tax adjustment on underpaid taxes and the corresponding late interest payment in the following circumstances:
- Transaction between an individual and his/her related parties that does not comply with an arm’s length principle and results in underpaid taxes of the individual or the related parties with no justified reason;
- An enterprise established in a country or jurisdiction that has lower tax rates controlled by a tax resident individually or jointly by a tax resident individual and a tax resident enterprise ; or
- Inappropriate tax benefits obtained by an individual through other unreasonable business purpose.
As the first information exchange on individual accounts of non-residents with high net worth has been carried out by Chinese tax authorities in September 2018, Chinese tax authorities would receive the exchanged information of Chinese tax residents from other participated countries or jurisdictions. Increasing transparency in the tax administration system may result in higher tax risks for Chinese tax residents who have any potential tax non-compliance.
5. IIT Filing Obligation
Following the consolidation of income and changes in the computation of IIT payable, the IIT filing obligations of taxpayers are revised in the IIT Law, 2018. The below table summarizes the filing obligation and deadline for all types of income that the taxpayer has with a withholding agent.
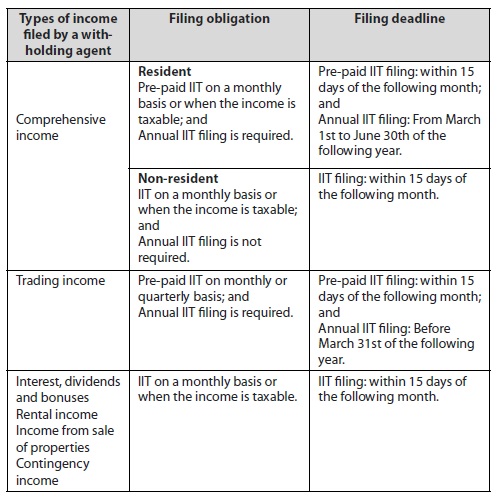 In addition to the above conditions, there are a number of situations that may require the taxpayer to file and pay the IIT with the competent tax authorities by themselves:
In addition to the above conditions, there are a number of situations that may require the taxpayer to file and pay the IIT with the competent tax authorities by themselves:
- Non-residents that have derived salary income from two or more employers in China shall file IIT on a monthly basis by themselves with the competent tax authorities respectively within 15 days of the following month in which the income is received;
- In case that the withholding agent fails to perform the withholding liability, the taxpayer shall file and pay the IIT to the competent tax authority by June 30th of the following year, unless the taxpayer is noticed by the tax authority on an earlier date of payment;
- Taxpayers that do not have a withholding agent shall file and pay the IIT to the competent tax authority within 15 day of the following month;
- Resident individual who derives overseas income shall file and pay the IIT to the competent tax authority between March 1st to June 30th of the following years; and
- Taxpayers who have immigrated shall perform tax clearance with the competent tax authority before de-registration of Chinese nationality.
6. Tax Identification Number For Taxpayers
Tax identification numbers for Chinese nationals are the national identity numbers, while taxpayers who do not have the national identity numbers will be provided with tax identification number by the tax authority.
7. Enhanced Communication between Chinese Government Authorities
Government authorities shall provide information to tax authorities for assistance in identifying the tax identification number, tax resident status, financial account information and information related to the Additional Special Deduction Items.
Conclusion
IIT Law 2018 is a remarkable revolution in the Chinese Taxation, which would have significant impact on the taxpayers and the withholding agent in a number of ways:
- Tax residents that have China-sourced income and overseas-sourced income will face a challenge for being taxed in China on the worldwide income with enhanced transparency in information exchange of financial accounts between Chinese tax authorities and tax authorities in participated countries or jurisdictions.
- Expatriates are more likely to become a Chinese tax resident with the shortening period of tax resident assessment.
- Lower and middle income Chinese employees would have significant IIT savings from the salary income after the implementation of IIT Law 2018, while high income Chinese employees may have limited benefits from it.
- Chinese employees who are eligible for Additional Special Deduction Items may further reduce their IIT burden.
- Chinese individuals who plan immigration to another country shall pay special attention to tax compliance status, which could have adverse influence on immigration plan.
- Complexity in withholding IIT filing would be increased significantly for Chinese employers. The human resource department shall prepare in advance in response to the number of changes in the IIT Law 2018, such as the annual IIT filing, Additional Special Deduction Items and tax resident status of employees.